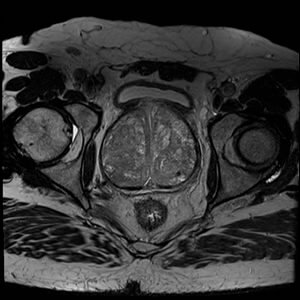
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) uses a magnetic field, radiofrequency pulses, and a computer to produce detailed pictures of the body. Doctors use Prostate MRI to evaluate the extent of prostate cancer and determine whether it has spread. They may also use it to help diagnose infection, conditions you were born with, or an enlarged prostate. Prostate MRI does not use radiation. It provides images that are clearer and more detailed than other imaging methods. Multiparametric (Mp-MRI) is an advanced form of imaging. It uses three MRI techniques to provide anatomical pictures and information on the function of the prostate gland. This helps determine whether cancer is present and, if so, whether it is aggressive and if it has spread. Mp-MRI assesses water molecule motion (called water diffusion) and blood flow (called perfusion imaging) within the prostate. This helps your doctor tell the difference between diseased and normal prostate tissue. Occasionally, MRI of the prostate is used to evaluate other prostate problems, including:
*Infection (prostatitis) or prostate abscess
*An enlarged prostate, called benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH)
*Abnormal conditions present at birth
*Complications after pelvic surgery
Limitations of Prostate MRI
MRI cannot always distinguish between cancer and inflammation or the presence of blood products within the prostate. Blood may sometimes appear due to a prostate biopsy. To avoid confusing any bleeding with cancer, your doctor may wait six to eight weeks after prostate biopsy to perform prostate MRI. This will allow any remnants of bleeding to resolve.
A prostate MRI can detect if a cancer is growing outside the walls of the prostate gland or into nearby structures, such as the seminal vesicles or bladder. This is a sign of possible metastatic disease. However, the exam cannot tell if a cancer has spread distantly into other organs outside the pelvis. If you are a high-risk patient or a patient with biochemical recurrence, your doctor may perform PSMA PET/CT, a test that can accurately detect the spread of prostate cancer to anywhere else in the body.
A Prostate MRI exam typically costs more and may take more time than other imaging exams. Talk to your insurance provider if you have concerns about the cost of MRI.